
| Chungbuk National University Researchers Propose a Novel Electrocatalyst Design for Improving Hydrogen Production | |||||||||||||||
| Writer | 관리자 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chungbuk National University Researchers Propose a Novel Electrocatalyst Design for Improving Hydrogen Production
The proposed design highlights the synergistic effects of both intrinsic and extrinsic improvements for anion exchange membrane electrolysis
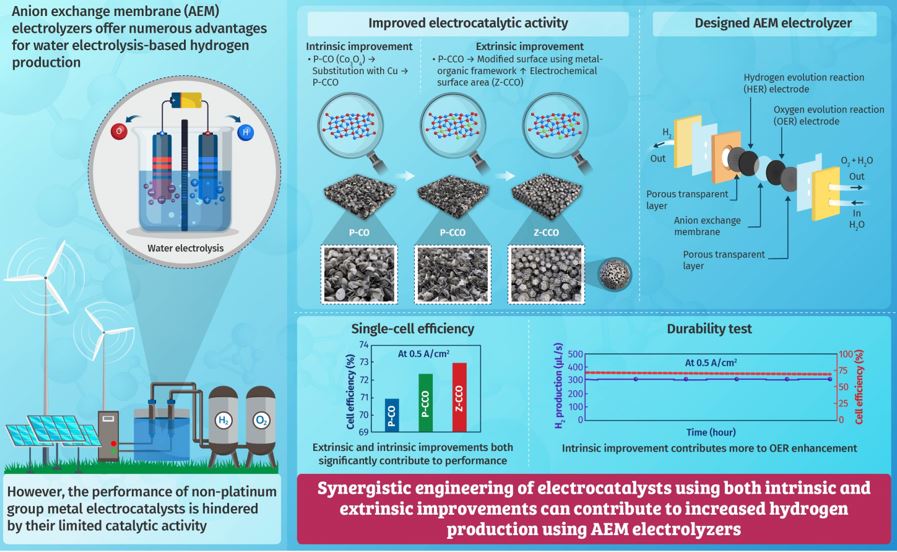
Water electrolysis is a leading technology for the eco-friendly production of hydrogen. However, current electrolyzers suffer from either low efficiency or high costs due to expensive platinum-based electrocatalysts. Now, a team of researchers has proposed an innovative non-platinum group metal electrocatalyst design, incorporating both intrinsic and extrinsic enhancements. This novel design significantly enhances the performance of next-generation anion exchange membrane electrolyzers and could lead to the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a fuel. Hydrogen is a promising clean alternative to fossil fuels and is gaining attention as a key player when considering sustainable sources of energy. It has the highest energy density of any fuel and only leaves water vapour as a residue after combustion. The process of water electrolysis, where electric current splits water into hydrogen and oxygen, is considered as a leading technology for hydrogen production. Moreover, when coupled with renewable power sources, it ensures eco-friendly and sustainable hydrogen production.
However, current commercial water electrolysis technologies, such as alkaline water electrolyzers (AWEs) and proton-exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolyzers, face certain drawbacks. AWEs have low energy efficiency, while PEM water electrolyzers, though more efficient, use expensive platinum group metal (PGM) electrocatalysts. Anion exchange membrane (AEM) electrolyzer is a recent addition to the list of next-generation water electrolysis technologies, offering high energy efficiency and low operating temperatures while utilizing economic non-PGM electrocatalysts. However, the limited catalytic activity of non-PGM electrocatalysts has hampered their widespread use.
In response, a team of Korean researchers, led by Professor Yoo Sei Park from Chungbuk National University, has now developed a groundbreaking non-PGM electrocatalyst design to boost AEM electrolyzer performance. Providing a rationale for the study, Prof. Park says, “The low efficiency of current electrolysis technologies has hindered the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a fuel. In this study, we proposed a design for an electrocatalyst that utilizes the synergistic effects of both intrinsic and extrinsic improvements, enhancing the efficiency of next-generation AEM electrolyzers.” Their study was made available online on July 31, 2023, and published in Volume 472 of the Chemical Engineering Journal on September 15, 2023.
Two main approaches can be used for improving the activity of electrocatalysts—intrinsic and extrinsic improvements. Intrinsic improvements involve increasing the inherent activity of electrocatalysts via methods like introducing defects or doping. On the other hand, extrinsic improvements focus on increasing the surface area of the electrocatalysts to enhance the contact area with the reactants. The team utilized copper-cobalt oxide electrocatalyst and enhanced its intrinsic activity by substituting copper with Co3O4 (P-CO), resulting in P-CCO. Furthermore, P-CCO was extrinsically improved through surface modification using a metal-organic framework, creating Z-CCO with a large electrochemical surface area.
The team then conducted experiments to study the effects of the improved electrocatalyst on the performance of an AEM electrolyzer. Both intrinsic and extrinsic improvements significantly enhanced the performance of AEM electrolyzer, leading to increased energy efficiency and reduced activation losses, thus improving hydrogen production. Both improvements resulted in enhanced oxygen evolution reaction (OER), a critical factor in overall electrolysis performance. Interestingly, intrinsic improvements were found to have contributed more to OER enhancement. These results clearly highlight the importance of utilizing the synergistic effects of both intrinsic and extrinsic improvements for efficient hydrogen production using AEM electrolyzers.
Stressing the significance of the study, Prof. Park states, “This research marks a significant step towards the commercialization of AEM electrolyzers and therefore widespread adoption of hydrogen as a fuel. The resulting improvements in hydrogen production hold immense potential, with applications in diverse areas such as hydrogen-powered vehicles, railways, environment-friendly urban power plants, and more.”
In summary, these findings translate into significant advancements in electrocatalyst design, paving the way for a hydrogen-powered future!
Reference
About Chungbuk National University Established in 1951 in Cheongju, South Korea, Chungbuk National University (CBNU) proudly stands as one of the ten Flagship Korean National Universities. Guided by the core values of Harmony, Dignity, and Future, CBNU envisions a dynamic future driven by the collaborative spirit of its vibrant community. Having produced over 150,000 graduates since its inception, its alumni actively contribute to societal development. Positioned advantageously at the heart of the nation, CBNU is celebrated for its central location—a key strength. Currently ranked first for student satisfaction nationwide, the university aspires to soar among the top 100 in Asia and the top 10 in Korea, embodying a commitment to excellence and progress.
About Professor Yoo Sei Park Yoo Sei Park is currently an Assistant Professor in the Department of Advanced Material Engineering at Chungbuk National University. He received his Ph.D. degree from the Pusan National University and subsequently completed a postdoctoral fellowship at Kansas State University. His research group focuses on developing advanced materials for energy conversion devices such as electrolyzers and fuel cells. He has published more than 40 research papers, which have been cited almost a thousand times. |
|||||||||||||||
| Attachments | |||||||||||||||